OpenFHE CI/CD Developers Guide
The GitHub Documentation is the best resource for syntax, feature detail, and abilities of the CI/CD.
In order to make modifications to reuseable workflow or actions the
CI/CD changes must be made to the [github-ci][5] branch. This branch
is specially protected, and the OpenFHE repository uses references to
the branch for reuseable workflows and actions.
For changes to what happens for the Custom, Main, Manual, or Pull-Request the files must be updated on the main branch.
├── .github
│ ├── actions <-- Custom GitHub actions
│ │ └─ default_builder <-- Custom GitHub actions to bootstrap the build
│ │ └── action.yml <-- Custom action file, defines the steps for a given configuration, cmake -> build -> unittest -> benchmark -> extras
│ ├── workflows <-- GitHub workflows(pipelines)
│ ├── custom.yml <-- Runs on-demand a single build of a custom configuration (this can turn all the knobs)
│ ├── main.yml <-- Runs when a branch is merged to main, uses reusable_workflow
│ ├── manual.yml <-- Runs on-demand with parameters
│ ├── pull-request.yml <-- Runs when a pull-request is created, uses reusable_workflow
│ └── reusable_workflow.yml <-- A workflow that handles the default builds and tests the important configurations, uses default_builder/action.yml
Actions
GitHub Actions are used to create function like abilities to the CI/CD. Thus reducing the scripting, lines of code, and complexity of the workflows. There is currently a single action to help build and test a given configuration .github/actions/default_builder/action.yml.
Default Builder
The default builder handles the setup, build, and running of binaries
(such as unittests and benchmarking) for a single configuration. The
flow of the Default Builder actions is:
Cmake configuration based on inputs
Build the configuration
Run unittests on the configuration
If benchmarking is requested via inputs run the benchmarks (takes a long time)
If extras are requested via inputs run the extra binaries
The actions are flexible as when can pass inputs which can be seen
in first section of the
.github/actions/default_builder/action.yml.
These inputs can be used throughout the action.yml to change behaviour.
Note
For more info on GitHub Actions in general please visit Learn GitHub Actions. The remainder of the action description will be specific to our implementation and use of GitHub Action features.
Current Action Inputs
We currently have the following inputs supported:
module_name - friendly string identifier for the configuration
cmake_args - fully customizeable string to override all other arguments
native_backend - sets the NATIVE_SIZE
mathbackend - set the MATHBACKEND
with_debug - enables the Debug build type
with_tcm - enables TC malloc
run_extras - enables the build and executation of extras.
with_nativeopts - enables native optimizations
run_benchmark - runs benchmarking
Adding New Inputs
To add a new input to the action it will need to be added to the
inputs section in the
.github/actions/default_builder/action.yml.
There is a constraint of 10 inputs, so care needs to be taking when
selecting inputs. Select that the type of the input for your input and
choose a default value that will not alter the previous behavior of the
important workflows After adding the parameter to
action.yml
you must set it using the with field, shown below, in any workflow
that you want to use the new parameter.
Defining a new input
name: 'Default Builder'
inputs:
my_new_input:
description: "Example of how to add a new input to the action"
type: string
default: ''
Using the input
uses: ./.github/actions/default_builder
with:
module_name: mb4_tcm
mathbackend: 4
with_tcm: true
run_extras: true
my_new_input: 'Do something new!'
Using the input value in the action procedure
runs:
...
run: |
echo "New input has value: ${{inputs.my_new_input}}"
The ${{}} is how the procedure can access the passed in value
Workflows
When designing the our workflows for OpenFHE we took the approach of bundling multiple configurations together. This influenced how the action.yml was designed, as we want to have the server configure, build, and run outputs without needing to pass artifacts around. Previously we had done all the builds for every configuration, then ran all the unittests for all the configurations, etc. This required over 20GB of artifacts be passed around. This means that each conifguration must build and pass all tests before another build can be evaluated.
Note
For more general information on GitHub Workflows please visit Using Workflows
There are 5 total Workflows:
Custom - Used to kick off a single build and test that can turn all the knobs.
Main - Used to extensively test pushes to the main branch and publish docs.
This also runs if pushes are made to the github-ci branch to allow testing and development of the CI. -
Manual - Used to do a batch of builds with a control over compilers, native size, configurations
Pull-Request - Used to test any pull-requests generated, this tests a healthy number of configurations but is not as extensive as Main.
Reuseable Workflow - This is not run from the GitHub UI, but instead is used to allow
pull-requestandmainworkflows to use a large portion of shared code.
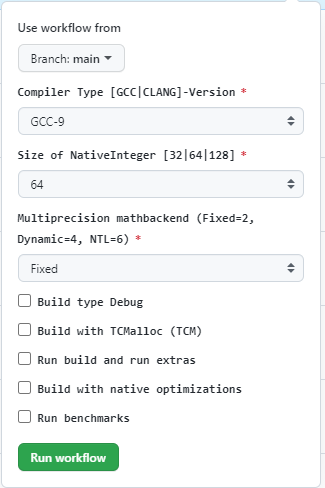
Custom Workflow
The custom workflow allows to select a number of options that are
supported and worth testing on a server. See the diagram below for the
options. All the options are created in the
.github/workflows/custom.yml
file under the on.workflow_dispatch.inputs property. The jobs
property is short and sweet for this workflow as it is only going to
kickoff a single default_builder action with the corresponding
option values. This workflow essentially gives the UI direct access to
the default_builder.
Note
There is a limit of 10 inputs.
JSON Maps
There are two important JSON maps in the Custom
Workflow to map the string input options, as the
key, to a corresponding cmake/action string value to pass onward. The
value for each map pair is corresponds to the lower level requirements,
thus whatever the option is driving is what the map’s value is derived
from. This is why the MATHBACKEND is a number value and the
COMPILER is a direct cmake argument string. Currently to (and for
simplicity this will likely remain) set the compiler the cmake_arg
override argument is used to set the desired compiler. For more info on
the compiler map visit section Compiler
Selection
Warning
Before adding new compiler options developers must ensure that the server as the compiler installed and match the path correctly in the JSON map.
example JSON map definition
env:
MATHBACKEND_MAP: >-
{
"Fixed" : "2",
"Dynamic" : "4",
"NTL" : "6"
}
Passing json map’s value to custom action
jobs:
default:
# ...
- name: default
uses: openfheorg/openfhe-development/.github/actions/default_builder@github-ci
with:
# ...
mathbackend: ${{ fromJson(env.MATHBACKEND_MAP)[github.event.inputs.mathbackend] }}
# ...
Warning
The map’s keys are not linked to the inputs options, this must be manually kept in sync.
Pull-Request Workflow
The pull-request.yml defines the Pull-Request Workflow. The Pull-Request Workflow is run whenever under 2 conditions: first when a pull-request is opened and whenever changes are pushed to that branch will the pull-request is open. The workflow runs on the branch linked to the pull-request. This is defined by the following code snippet.
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- main
The Pull-Request Workflow only runs one job which is the Reuseable
Workflow with all inputs set to true.
Notable differences * Doesn’t publish docs * Doesn’t do
NATIVE_SIZE=128 or clang compiler tests
Main Workflow
The main.yml defines the Main Workflow, which runs when changes are pushed to main. The Main Workflow is also run when changes are pushed to the branch github-ci but this is for testing and development purposes of new CI/CD features. This is defined by the code snippet:
on:
push:
branches:
- main
- github-ci
The Main Workflow use the Reuseable Workflow
for the bulk of the jobs. In addition this workflow has 2 other
important testing jobs are run using the
default_builder action to test
NATIVE_SIZE=128 (mb2_128) and compilation with clang (mb2_clang).
And lastly this workflow has a job that pushes the doxygen generate
documentation to a specific branch,
gh-pages
in the repository, is best access through the
github-pages.
Reuseable Workflow
The reuseable_workflow.yml defines the Reuseable Workflow, which is not run directly through GitHub pushes, pull-requests, or UI interactions. Instead this workflow encapuslates the bulk of the CI/CD that should be use in multiple workflows. This workflow is declared reuseable by the following code snippet:
on:
workflow_call:
inputs:
# ...
Where workflow_call property enables other workflows to run this
entire workflow through the following calling squence:
jobs:
call:
uses: openfheorg/openfhe-development/.github/workflows/reuseable_workflow.yml@github-ci
with:
# ...
The Reuseable Workflow makes use of the Default
Builer to run configuration checks for a number of
configurations that correspond to the Reuseable Workflow’s inputs.
Inputs
mb2_debug
mb2_tcm
mb4_noflag
mb4_debug
mb4_tcm
mb6_ntl_noflag
mb6_ntl_debug_tcm
mb6_ntl_tcm
Each of these inputs is a boolean that enables or disables the
corresponding job. There is one job that is implicitly always enabled,
default, which is also mb2_noflag if the same naming convention was
used. The default job is the portable build and what is created when
no inputs are given to cmake. This allows other workflows to turn off
pieces of the workflow if not desired. This is done by using the inputs
in the following way:
mb2_tcm:
needs: [default, mb4_noflag, mb6_ntl_noflag]
runs-on: [self-hosted, Linux, X64]
# This is the line that enables/disables the mb2_tcm job!
# There for everything after this line, for this indented section, is skipped
if: inputs.mb2_tcm
steps:
- name: Checkout Code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: mb2_tcm
uses: openfheorg/openfhe-development/.github/actions/default_builder@github-ci
with:
module_name: mb2_tcm
mathbackend: 2
with_tcm: true
run_extras: true
Manual workflow
The manual workflow allows for more configurations to be tested and the
flexibility to test unique combinations. Should a new parameter be added
it will need to be added to the on.workflow_dispathc.inputs section.
Currently we have inputs of type options which will yield a dropdown
and boolean which will yield a toggle box. There is a third type
GitHub supports which is a string that we don’t use on purpose.
Currently the default build is always run, and like the main and pull-request workflows the other builds depend on it. The difference is that each of the secondary build configurations can be enabled/disabled. By default none of the secondary builds are enabled. The code that enabled this is shown in the Enablable Build
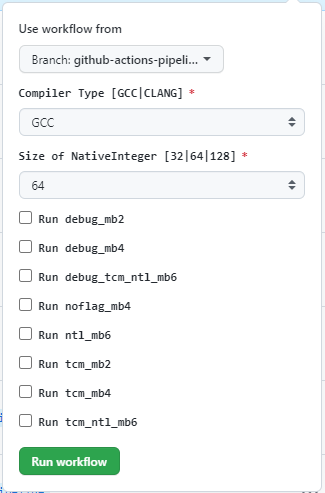
Enablable Build
The code that allows the individual builds are a combination of the
boolean inputs and an if in the jobs. See the example below for
the debug_mb2
input section
debug_mb2:
description: 'Run debug_mb2'
type: boolean
required: true
default: 'false'
The type key defines this input to be a checkbox, true or false, and
the default unchecks/disables this by default. This key itself,
debug_mb2, will be what is used later to enable/disable the job to
run.
job section
debug_mb2:
needs: default
if: ${{ github.event.inputs.debug_mb2 == 'true' }}
runs-on: [self-hosted, Linux, X64]
env:
The needs key, first line in the debug_mb2 job, is to create a
dependancy on the default, thus this will run after the default
configuration completes. The if key, second line, is where we
conditionally run the job, this logic uses the input parameter
debug_mb2 and skips the rest of this second if it is false.
Compiler Selection
Selecting the compiler is a bit convoluted, the JSON syntax is used to
create a map between compilers and the cmake options to use the compiler
selected. This map uses the
workflow_dispatch.inputs.compiler.options as the key, and the cmake
equivalent option as the value.
Note
This is linked by the definition of COMPILERS_MAP in the jobs
Modifying the input will require modification of all env.COMPILERS_MAP
Because we want to support many compilers and versions we will need to expose more pairs in the future. For now the key things to understand is the map and how it’s used.
Below is how we’ve created the map, we use JSON syntax in the yml and do
so on multiple lines with >- operator.
Compiler map definition
COMPILERS_MAP: >-
{
"GCC" : "-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=/usr/bin/g++-9 -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/usr/bin/gcc-9",
"CLANG" : "-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=/usr/bin/clang++-10 -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/usr/bin/clang-10"
}
Below is a snippet to parse the cmake options from the selected compiler input
Compiler map value access by key input
cmake_args: ${{ fromJson(env.COMPILERS_MAP)[github.event.inputs.compiler] }}
Note
This can’t be done in the .github/actions/default_builder/action.yml, as access to the
fromJsonfunction isn’t available in that scope.
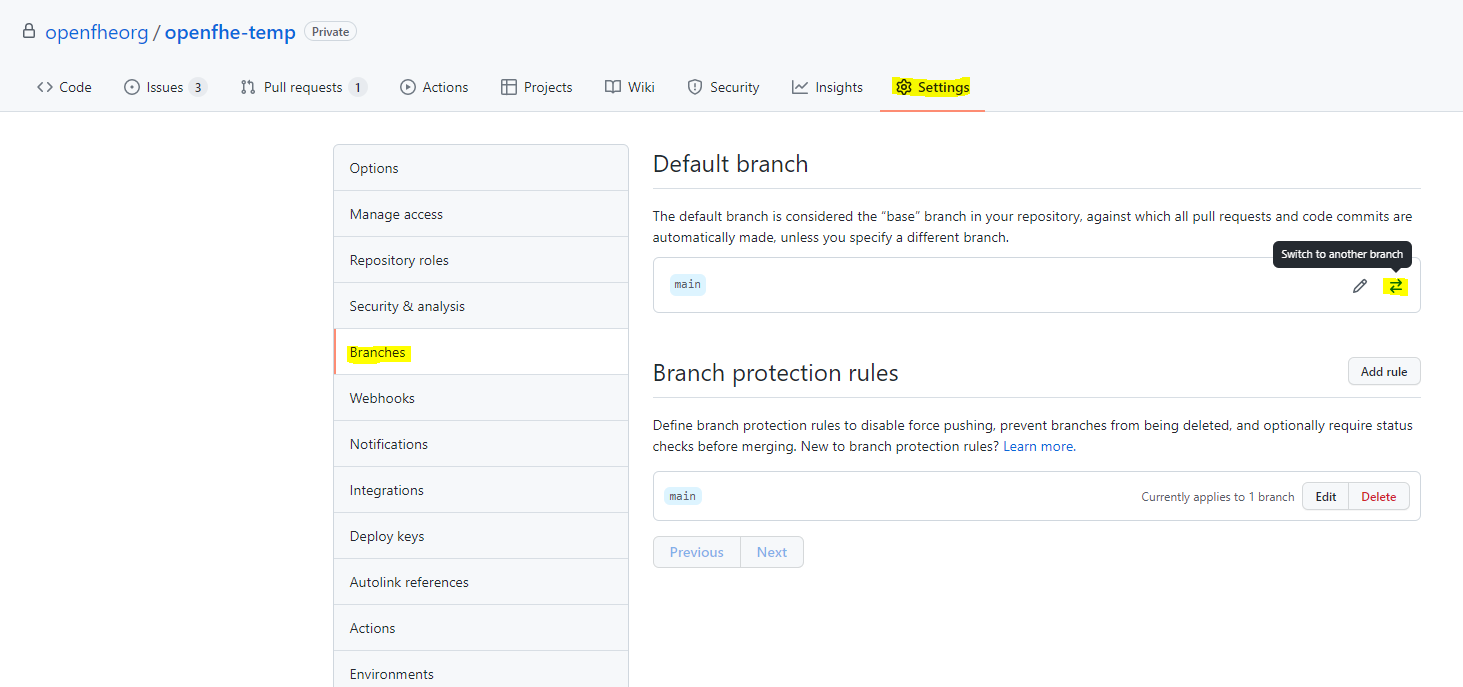
Modifying or Adding New Workflows
When developing a new workflow it is required that the Default Branch
be set to whatever your development branch is to expose the workflows,
and thus reverted on completetion. This can be done by navigating to the
repository’s Settings > Branches and selecting a new Default
Branch as shown below.
When modifying an existing workflow there are a few approaches for testing your changes. If the changes are to pull-request as soon as a pull-request is generated.
Please take care with naming new workflows - Follow the design pattern already in use, where the Workflows name and the corresponding YML file are related via the pattern:
YML File: new-workflow.yml
Workflow Name:
name: New Workflow
Setup GitHub Actions Runner
Setup Linux Server for OpenFHE
OpenFHE To see how to setup linux_platform_packages.sh in the repository, or run it on your linux platform.
Note
This is for an Ubuntu 20.04 distribution
Launch an EC2 Instance using AWS CLI
aws ec2 run-instances \
--image-id <AMI-Id> \
--count 1 \
--instance-type <EC2-Type> \
--key-name <Key-Pair-Name> \
--subnet-id <Subnet> \
--security-group-ids <Security-Group-ID>
--user-data file://user-data.txt
This will create an EC2 instance.
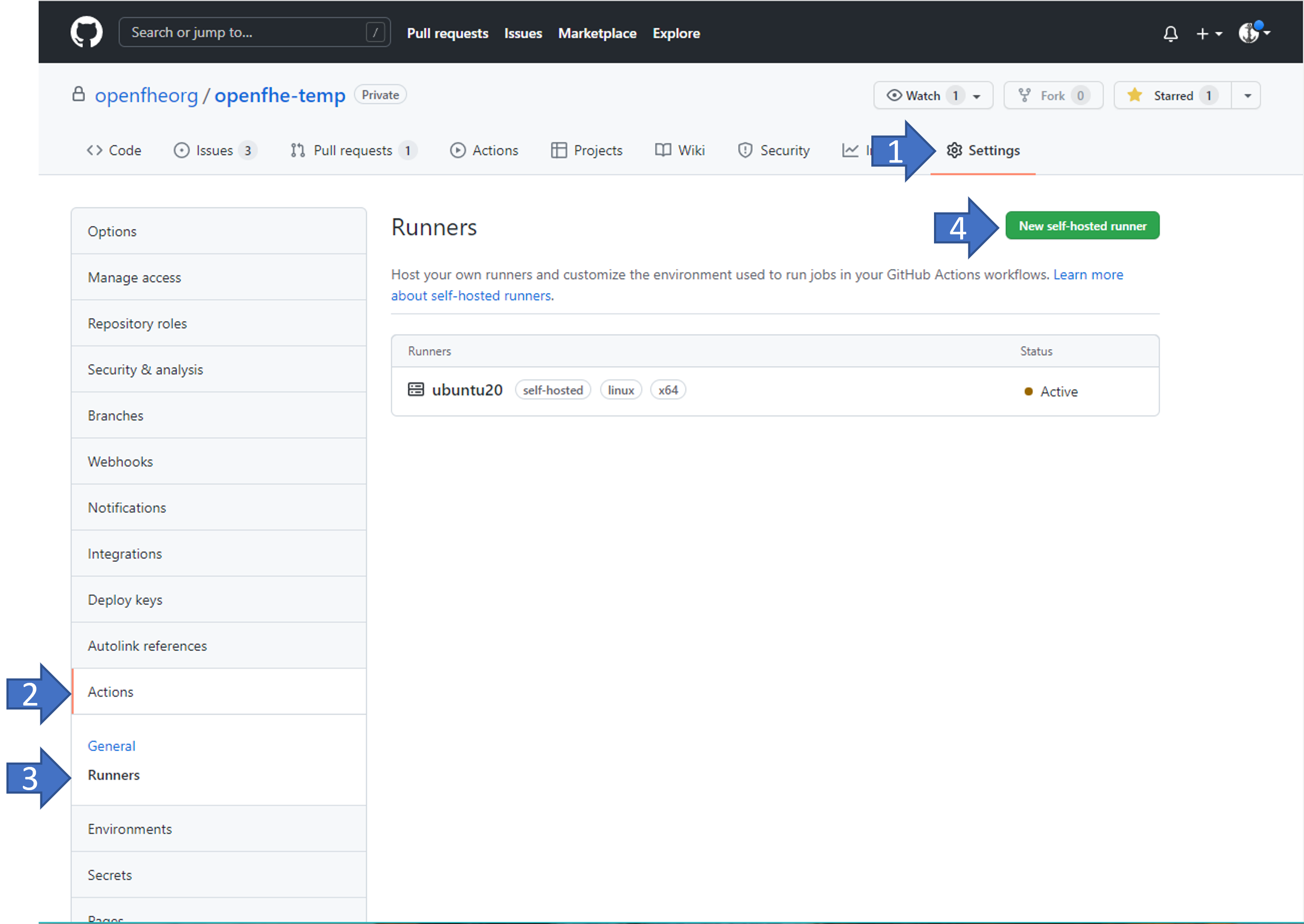
Configure the EC2 Instance as GitHub Actions Runner
Refer this documentation, adding-self-hosted-runners, on how to self-hosted runner to a repository. Below is an image of how to verify that a self-hosted runner is linked to the repository.